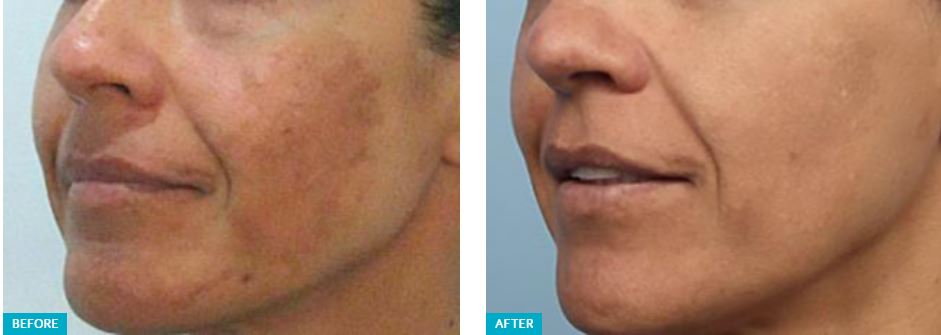
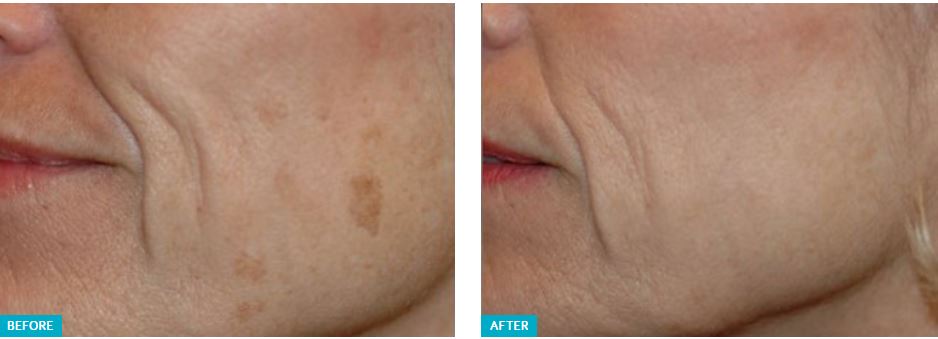
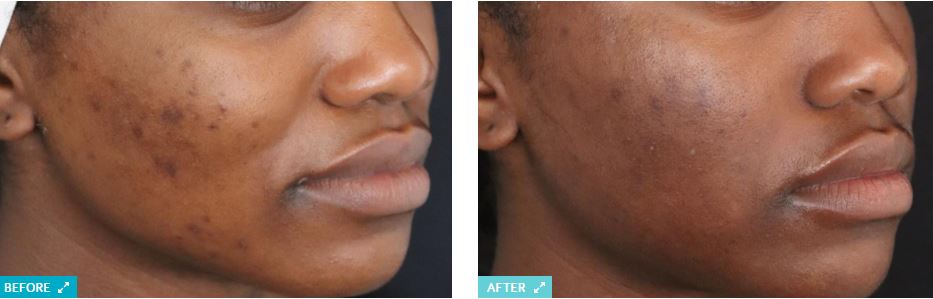
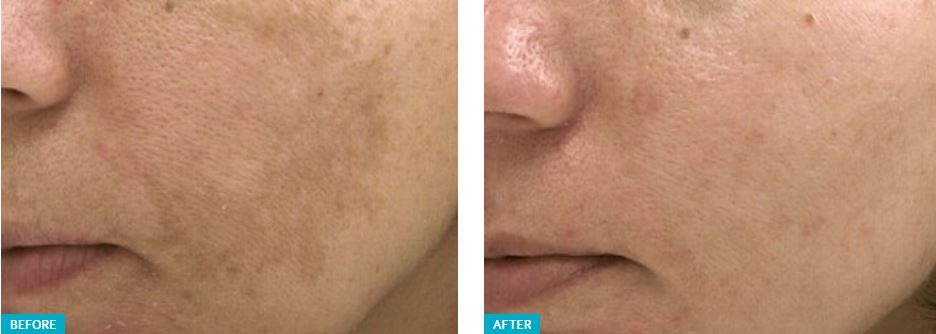
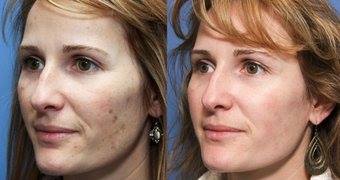
HYPERPIGMENTATION
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Simply put, hyperpigmentation is darker than usual skin. Flat spots or patches of increased pigment can occur anywhere on the body, especially where skin is exposed to the sun, and contribute to an uneven skin tone.
The excess pigment (aka melanin) may be deposited in the skin’s top layer (superficial epidermis) or deeper in the dermis of the skin. The deeper the pigment, the tougher it is to treat.
The condition is common in all skin tones, but it’s particularly prevalent in olive and brown skin, where high levels of melanin are already present.

What causes hyperpigmentation?
Dark spots and patches of hyperpigmentation can develop due to a variety of factors, including acne, hormone fluctuations, stress, and sun damage.
When skin breaks out, the inflammation and the injury to the tissue can increase pigment production as cells called melanocytes are provoked into producing melanin. This is known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). After a blemish heals, a red, purple, brown, or black spot is left behind, like a shadow, in its place.
Beyond acne, PIH can be caused by anything that irritates the skin, like eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, allergic reactions, or bug bites. Additionally, cosmetic treatments that evoke an inflammatory response, including lasers and strong chemical peels, come with a significant risk of PIH.
Hyperpigmentation can also show up as irregularly shaped brown or gray patches, known as melasma or chloasma. This type of discoloration is caused
 by hormonal changes, stress, and medical conditions (like thyroid disease or lupus) that may cause skin to be more photosensitive.
by hormonal changes, stress, and medical conditions (like thyroid disease or lupus) that may cause skin to be more photosensitive.
Melasma can be unpredictable and especially difficult—sometimes almost impossible—to fully resolve. It’s caused by often unavoidable internal factors, and the pigment can be trapped deep down in the skin. It’s more common in women and often crops up during pregnancy when estrogen and progesterone overstimulate melanin production. Birth control pills and hormone replacement medications may also trigger it. Melasma usually appears on the forehead, nose, cheeks, and upper lip (“the melasma mustache”).
Sun exposure increases melanin production too, creating brown sunspots, age spots, and liver spots while worsening both PIH and melasma. UV light speeds up the production of melanin. These brown spots of hyperpigmentation can vary in size and shape, and they’re most common in the areas that see a lot of sun, such as the face, shoulders, and hands.
TYPES OF TREATMENTS
What are the most effective treatments for hyperpigmentation?
- Lightening creams.
- Face acids.
- Retinoids.
- Chemical peel.
- Laser peel.
- IPL therapy.
- Microdermabrasion.
- Dermabrasion.
Lightening Creams
Lightening creams are over-the-counter (OTC) treatments that work with select ingredients to help decrease pigmentation. Many of these creams are available in stronger prescription forms. They’re usually applied once or twice a day to help lighten the skin over time. Topical treatments for lightening also come in gel form.
Common ingredients found in OTC lightening products include:
- hydroquinone
- licorice extract
- N-acetylglucosamine
- vitamin B-3 (niacinamide)
Who should try this?
Lightening creams or gels work best for flat spots, such as melasma or age spots. They’re effective for patches of discoloration on most skin types.
OTC products are accessible (and sometimes more affordable) options for hyperpigmentation, but these can take longer than professional treatments.
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using caution when purchasing OTC skin lighteners, as they may contain traces of mercury.

Face Acids
Face acids, or skin acids, work by exfoliating, or shedding, the top layer of your skin. Whenever you exfoliate your skin, new skin cells emerge to take the place of the old ones. The process helps even out your skin tone and makes it smoother overall.
Many face acids are available OTC at beauty stores and drugstores, but we recommend the Obagi line of NuDerm or Zo® Skin Health.
Popular ingredients include:
- alpha hydroxy acids, such as glycolic, lactic, citric, malic, or tartaric acid
- azelaic acid
- kojic acid
- salicylic acid
- vitamin C (in the form of l-ascorbic acid)
Retinoids
Derived from vitamin A, retinoids are among some of the oldest OTC skincare ingredients used. Their small molecular structure allows them to penetrate deep into the skin and treat the layers below your epidermis.
Retinoids can come in either a prescription or OTC formula. However, OTC versions tend to be weaker. If you don’t see any results after a couple of months, talk to your dermatologist about the prescription retinoid tretinoin (Retin-A).
Who should try this?
OTC retinoids may be safe for all skin tones, but you should double-check with your dermatologist if you have darker skin and plan on using these products long term.
It’s also important to note that retinoids are more often used to treat wrinkles than hyperpigmentation. This means that retinoids may not be the best first-line treatment.

Chemical Peel
A chemical peel uses acids at stronger concentrations to treat the desired area of skin. They reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation by removing the epidermis. Deeper versions may also penetrate the middle layer of your skin (dermis) to produce more dramatic results.
Although many chemical peels are available OTC, you might consider getting a professional-grade peel at your dermatologist’s office. These are more powerful, and they yield quicker results.
Due to their strength, in-office peels may also increase your risk for side effects. Talk to your dermatologist about your individual risks.
Possible risks with both at-home and in-office chemical peels include redness, irritation, and blistering. When used improperly, blisters or scars may also develop.
If you’re out in the sun on a regular basis, chemical peels may not be the best treatment option for you. Chemical peels cause your skin to be more sensitive to the sun’s rays. If you don’t adequately apply sunscreen and use other UV protection, the sun may worsen your hyperpigmentation. You’ll need to take extra precautions for at least one week after your last chemical peel.
Who should try this?
Chemical peels may work if you have:
- age spots
- sun damage
- melasma
- blotchy skin
They also work best for fairer skin tones, and they may provide faster results than face acid products.
Laser Peel
A laser peel (resurfacing) treatment uses targeted beams of light to reduce hyperpigmentation.
There are two types of lasers: ablative and non-ablative. Ablative lasers are the most intense, and they involve removing layers of your skin. Non-ablative procedures, on the other hand, target the dermis to promote collagen growth and tightening effects.
Ablative lasers are stronger, but they may cause more side effects. Both destroy elements in your skin to ensure that new skin cells grow back tighter and more toned.
Who should try this?
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach to skin resurfacing. Ablative lasers may work better for people with fair skin. For some people, non-ablative versions may cause the skin to darken instead of lightening. After your initial complimentary consultation, we will work with you to assess your discoloration and overall skin tone to select the best option for your skin.
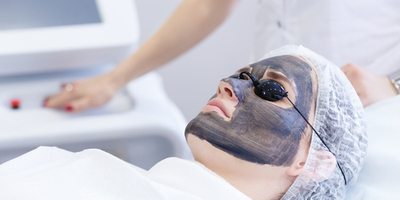
Intense pulse light therapy (IPL)
IPL therapy is a type of non-ablative (fractional) laser treatment. Also known as a photofacial, IPL therapy stimulates collagen growth within the dermis. It usually requires multiple sessions.
IPL is used for overall pigmentation issues, but flat spots especially respond to this treatment. It may also help reduce the appearance of wrinkles, spider veins, and enlarged pores.
Who should try this?
According to Emory Healthcare, IPL works best for people with fair skin.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is an in-office procedure used to treat hyperpigmentation that affects the epidermis only (superficial scarring).
During the procedure, your dermatologist will use a drill-like handheld tool with a wire brush or other abrasive attachment. The tool is then swiped across your skin to rapidly — but gently — to remove the epidermis. You may need multiple sessions to achieve your ideal result.
Who should try this?
Microdermabrasion works best on superficial scars. Your dermatologist can help you determine whether this treatment is right for you. It also works well for people with fairer skin.
Dermabrasion
Dermabrasion also involves the removal of your epidermis, but its effects continue down to part of your dermis.
While dermabrasion is sometimes used to smooth out wrinkles, the procedure has been historically used to address texture concerns. These include:
- acne scars
- age spots
- chickenpox scars
- injury scars
- sun damage
As with microdermabrasion, your dermatologist will use a drill-like handheld tool with a wire brush or other abrasive attachment. They’ll move the tool across your skin to rapidly — but gently — to remove your entire epidermis and the top part of your dermis.
Who should try this?
Dermabrasion may be a good option if you’re looking to decrease pigmentation at a faster rate than microdermabrasion.
It works best for fairer skin. People with medium skin tones may go on to develop further hyperpigmentation as a result of the procedure. The new patches of hyperpigmentation may lighten after about eight weeks.
What works best for each skin tone?
Skin tone can play a role in the intensity and length of hyperpigmentation treatments. As noted by Zeiva, people with fair, medium, and dark skin tones can use some of the same therapies, but people with darker skin need more time for the treatment to work.
Fair skin responds well to most hyperpigmentation procedures.
The following might be off limits if you tan easily or have darker skin:
- high-beam lasers
- IPL therapy
It’s importantly to note, that at Zeiva Professional Center, we specialise in laser therapies for darker skin tones.
Medium skin tones may find the following options helpful:
- chemical peels
- microdermabrasion
Darker skin might benefit from:
- glycolic acid
- kojic acid
- OTC lightening creams
- microdermabrasion
- lower-strength chemical peels
- laser treatments, but potentially over a larger number of sessions
Topical treatments generally take longer to produce visible results. Patience is key with any treatment option.
Real Clients – Real Results
Daniella
★★★★★
“Great experience!! Zeiva is so knowledgeable. My daughter and I are definitely going back!!”
Dorothy
★★★★★
“Very professional! Just one treatment and I believe I already see an improvement!”
Helga
★★★★★
“I had the best experience here at this center. Very clean. Very professional. They went above and beyond, and I will definitely stay a long-time customer.”
Betsy
★★★★★
“I ❤ this place! Very professional and great prices. Excellent service!”
TREATMENT
We can help…
We’re here to help you achieve your desired look.
A free consult can help you identify the best treatment for your hyperpigmentation, and we’ll work with you to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
No matter what treatment you ultimately choose, it’s important to protect your skin from further sun damage and hyperpigmentation. Wearing sunscreen every day is a must. You should apply sunscreen every morning — even when it’s cloudy! — and reapply as needed throughout the day. Be sure to use a sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher.
Schedule a consultation with one of our technically certified cosmetic estheticians.